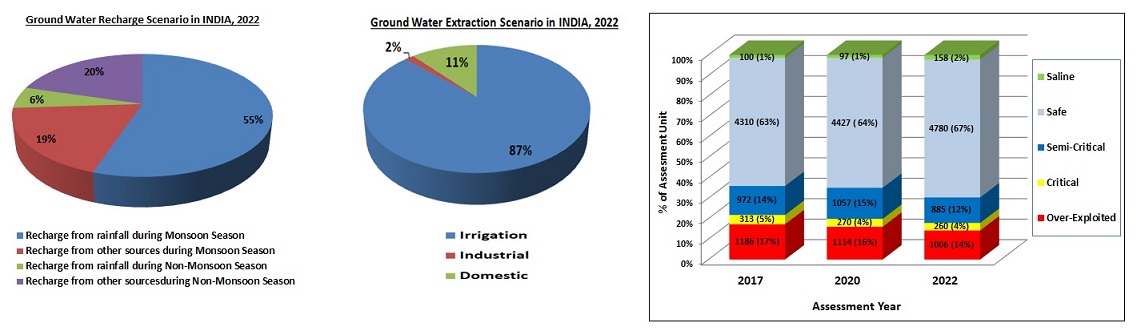
Peter Drucker, the famous management guru said, “If you can't measure it, you can't manage it.” It is true for ground water as well. Sustainable development of ground water resource requires precise quantitative assessment based on valid scientific principles. . The Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India is periodically assessed by Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) jointly with the State / UT level agencies. This exercise, comprises assessment of Annual Ground Water Recharge, Extractable Ground Water Resource, Ground Water Extraction. Stage of ground water extraction in an assessment unit is calculated as the ratio of annual ground water extraction to annual extractable resource. Based this the assessment units are categorised as Safe, Semi-critical, Critical or Over-exploited. In addition to this, assessment units with predominantly saline ground water are categorised as “saline”.
 |
| Watch this short film on ground water resource assessment. |
Periodic Assessment of dynamic ground water resources is done jointly by CGWB and the respective state governments. Methodologies used for assessment of ground water resources and assessment results (in form of reports) are summarised in the following paragraphs
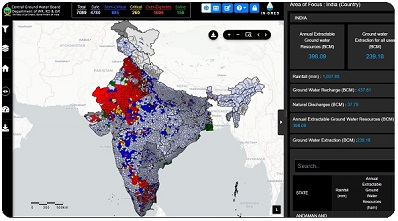
A web-based application “INdia-Groundwater Resource Estimation System (IN-GRES)” has been developed by CGWB in association with IIT-Hyderabad. IN-GRES provides a common and standardized platform for GW Resource Assessment for the entire country (Central and State Governments). INGRES was used for ground water resources assessment for the first time in 2020. INGRES is a GIS based platform for assessment as well as dissemination of results. Use the following link to access INGRES.
Country wide assessment of ground water resources poses challenges especially in terms of data availability and maintaining uniformity and comparability of the results. Therefore, a trade-off between best scientific techniques and their applicability on a country scale is important. Ground water being a dynamic system, the methodology for assessment requires continuous updating keeping abreast with the evolution in technologies, improvement in data availability and demands of planning requirements. The first attempt for country wide assessment of ground water resources was made on adhoc norms in 1972. Subsequently, the Ground Water Overexploitation Committee in 1979 brought out a systematic methodology along with revised norms and procedures for categorization of areas. The methodology was further refined by Ground Water Estimation Committee, 1984 (GEC’84); Ground Water Estimation Committee, 1997 (GEC’97) and Committee on methodology for ground water resource estimation in hard rock areas, 2004. The Methodology was further revised in 2015.
For more information visit links below:
- Report of the Resource Estimation Committee, GEC-1997
- Ground Water Resource Assessment Methodology (GEC 97)-Detailed Guidelines
- Report of the Resource Estimation Committee, GEC-2015
- Ground Water Resource Assessment Methodology (GEC 2015)-Detailed Guidelines
- Assessment of Ground Water Resources- A Review of International Practices
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2023
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2022
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2022,Appendices
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2020
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2020, Appendices
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2017
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2013
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2011
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2009
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 2004
- National Compilation on Dynamic Ground Water Resources of India 1995
- Click Here for more State/U.T. wise reports on Dynamic Ground Water Resource Assessments