Geophysical investigations are used for exploration of groundwater and in delineating the underground structures which control the occurrence, distribution and movement of ground water. Application of geophysical techniques for ground water investigations on regular basis commenced in CGWB during the seventies. The Board has made extensive use of both the surface and the subsurface (well logging) geophysical techniques in the search of groundwater and proper construction of water wells. The findings of the geophysical studies, as a practice, are combined with the hydrogeological and geomorphologic investigations to place them on firm footing. The techniques have become an integral part of the ground water exploration programme.
As an integrated multi-disciplinary approach in ground water exploration studies, the role of geophysical surveys is vital. The chief aim of geophysical surveys is to understand the hidden sub-surface hydrogeological conditions accurately and adequately with respect to depth and formations favourable for ground water repositories. The integrated multi-disciplinary approach reduces the effective cost of drilling by pinpointing the potential drilling sites and helps in accurately designing the well assembly for tapping the fresh groundwater zones.
In CGWB, the surface geophysical surveys comprises of:
- Surveys,
- Ground - Transient Electromagnetic (G-TEM) Surveys
are carried out as an integral part of its activities, in different hydrogeological terrains of India, to assess, support, supplement and corroborate the National Aquifer Mapping (NAQUIM), Ground Water Exploration (GWE) studies and Short Term Water Supply Investigations (STWSI).
- The Resistivity Surveys comprising of Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES), Wenner Resistivity Profiling (WRP), Gradient Resistivity Profiling (GRP) and Multi-Electrode Resistivity Imaging Survey (2D / 3D Resistivity Imaging) are conducted for deciphering the depth and thickness of the potential groundwater zones, to generate sub-surface resistivity distribution etc.
- The Ground Transient Electromagnetic (G-TEM) surveys are carried out by using Monex GeoScope - terra TEM24 instrument, to demarcate fresh / saline water interface, depth to hard rock.
- Heliborne Transient Electromagnetic survey and other ground geophysical (ERT, TEM & EVRI) studies have been carried out in arid north western India in parts of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana States, for high resolution aquifer mapping and management. CGWB have a Heliborne Data Facility Center with dedicated workstations for AEM data processing, inversion and interpretation using Aarhus Workbench software.
- CGWB has microprocessor based Resistivity Meters, Multi Electrode Resistivity Imaging Systems, Very Low Frequency (VLF), Proton Precession Magnetometer (PPM) and Transient Electromagnetic (TEM) instruments to acquire geophysical data for aquifer mapping, artificial recharge and different hydrogeological / pollution / site investigation studies.
 |
 |
| Surface Geophysical Studies |
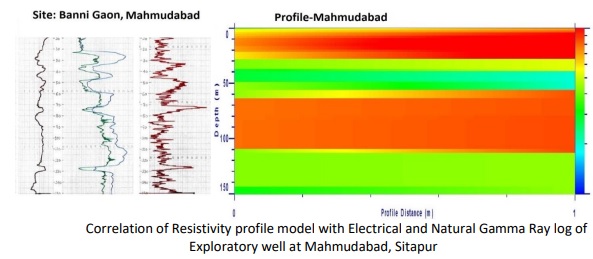
The Borehole geophysics is used in groundwater to obtain information pertaining to lithology, fractures, permeability, porosity and water quality so as to delineate subsurface disposition of aquifers. Borehole Geophysical Loggings are also carried out for deciphering the depth range of saturated sand, gravel formations for designing the well assembly by measuring Self Potential (SP), Single Point Resistance (SPR), Short Normal Resistivity (N16”), Long Normal Resistivity (N64”) and Natural Gamma (NG) parameters. Even, the depth ranges of saline groundwater zones are identified and marked for cement sealing and putting blank in the well assembly against that depth range for not tapping these zones. The proper positioning and condition of casing and screen pipes in a well can be rapidly evaluated with geophysical borehole logging.
Central Ground Water Board, Ministry of Jal Shakti and CSIR-NGRI, Hyderabad have signed a Memorandum of Agreement for High Resolution Aquifer Mapping and Management in Arid Regions of North Western India, by using advanced Heli-borne Geophysical Surveys and other scientific studies in parts of the States of Rajasthan, Gujarat Haryana, Punjab and Himachal Pradesh, covering an area of 3.88 lac sq./km. under the National Aquifer Mapping Programme (NAQUIM) with financial outlay of Rs. 54 Cr for Phase-I. The Heliborne Surveys have been proposed in two phases. During the Phase-1, 1.01 lakh sq.km was proposed in 2020-22, out of which 19020 sq.km considered priority areas covering Sikar, Jaisalmer and Jodhpur districts of Rajasthan, Kurukshetra and Yamuna Nagar districts of Haryana and remaining areas are normal.
The heliborne survey data has been obtained through a total of 40323 flight line km, 86 km through Earth Resistivity Tomography (ERT) surveys and Electrical Vector Resistivity Imaging (EVRI) have been used. The studies aimed at finding aquifer system with relatively fresh and saline zones, aquifer geometry of principal aquifer with demarcation of de-saturated and saturated aquifers, identification of paleochannels network and their linkage with the aquifer systems in the area, groundwater potential worthy sites for withdrawal of groundwater and water conservation structures through artificial or Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR). Remaining area of 2.87 lakh. Sq.km is envisaged under Pahse-2 for 2022-24. The reports on Geophysical Exploration in Desert for Ground Water and Summary Report on Heliborne Survey for High Resolution Aquifer Mapping in Arid Regions of North-Western India are provided in the link below:
Geophysical Exploration in Desert for Ground Water Summary Report on Heliborne Survey for High Resolution Aquifer Mapping in Arid Regions of North-Western India
MoA Signed between CGWB & NGRI on 21 Dec. 2020
Heliborne Survey Inauguration at Jodhpur on 5th Oct. 2021












