Ground water levels in a particular geographic location depend upon parameters like hydrogeological conditions, recharge and ground water extraction in that area. Ground water levels are measured in terms of depth below ground level. Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) is periodically monitoring the ground water levels throughout the Country on a regional scale, through a network of monitoring wells. State Governments also have their own ground water monitoring stations. All these water level data are stored at Water Information and Management System (WIMS) developed and maintained by National Water Informatics Centre (NWIC).
1. National Ground Water Monitoring Network – CGWB
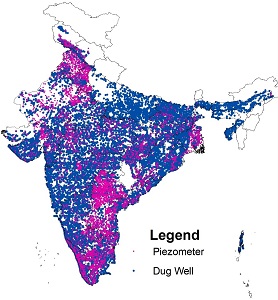
Central Ground Water Board monitors groundwater levels throughout the country on a regional scale, four times in a year during the months of March/April/May, August, November and January. For monitoring of ground water level, CGWB has a dedicated network of about 25000 monitoring stations called “National Hydrograph Network Stations (NHNS)”, which comprises open dug wells and purpose built bore/tube wells for water level monitoring called piezometers. CGWB has initiated automatic high frequency monitoring by installing Digital Water Level Recorders (DWLR) with telemetry systems under the National Hydrology Project (NHP). Total DWLRs proposed under NHP is 5260. The six hourly water level data recorded is being transferred to a central server through an online application Water Information Management System (WIMS) developed and maintained by National Water Informatics Centre (NWIC) under Ministry of Jal Shakti. NWIC has developed another web-based public platform, namely India-WRIS for data sharing and dissemination, where the water level data are finally shared to end users. In order to strengthen its monitoring network, CGWB has envisaged construction of 7000 piezometers under Public Investment Board (PIB) project and another 2000 piezometers under the (GWMR) Scheme. These piezometers will be fitted with Digital Water Level Recorders (DWLR) and telemetry system.
2. Climate Response Monitoring Network- CGWB
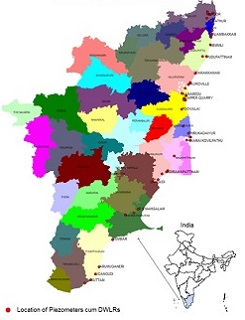
Central Ground Water Board (CGWB) has established a Climate Response Monitoring Network (CRMN), under National Hydrology Project, which is designed to serve as a measure of ground water conditions including quality with special focus on seawater intrusion all along the coastal tracts of Tamil Nadu & Union Territory of Puducherry. The primary purpose of the CRMN is to portray the effect of climate on ground-water levels and quality in unconfined aquifers or near surface confined aquifers that are affected by pumping or other anthropogenic stresses. The network includes 60 piezometers installed with telemetric Digital Water Level Recorders (DWLR’s) covering a length of 450 kms. The piezometers are constructed with variable depths ranging from 30 to 300 meters depending upon the aquifer characteristics with a distance from the coastline ranging from 100 meter to 34 kilometers, in order to demarcate the extent of seawater intrusion along the coast. The CRMN has the capability to display real time water level, quality (Electrical Conductivity) and temperature data every six hours. Sites are present in 12 districts of Tamil Nadu State and two regions in Union Territory of Puducherry. The data is transmitted on real time basis to Water Information Management System (WIMS) through RODC (Regional Office Data Centre) server in Central Ground Water Board, South Eastern Coastal Region, Chennai.
 |
 |
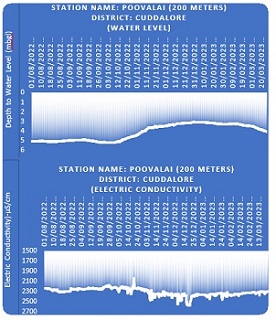 |
| Location of piezometers in Tamil Nadu Coast. The piezometers have been fitted with DWLRs with Telemetry system. | A piezometer in the field and the system at the Regional Office Data Centre | A representative hydrograph |
3. Other Monitoring Stations:
In addition to the above, State Governments also have their own ground water monitoring network. Under the National Hydrology Project (NHP), the state ground water monitoring networks are being strengthened by the construction of piezometers and installation of Digital Water Level Recorders with telemetry systems. Piezometers with Digital Water Level Recorders (DWLRs) are also being installed as a part of Atal Bhujal Yojana in the areas, where Atal Bhujal Yojana is operational. Ministry of Rural Development and the Ministry of Panchayati Raj, Government of India have jointly developed an App “Jaldoot App” for measuring the water level in Gram Panchayats.
1. Ground Water Yearbook
CGWB, based on periodic measurements of ground water levels, prepares ground water year books for the states as well as for the country as whole. Such yearbooks for individual years are available for download from CGWB Publications Repository (CGWB Pure). Yearbooks can be downloaded also using the following links:
2. India Water Resources Information System (India WRIS):
India Water Resources Information System (India WRIS) is an integrated platform for all water related information. The system is maintained by National Water Informatics Centre (NWIC).
Click here to Visit India-WRIS Portal
3. Water Information and Management System (WIMS):
Water Information and Management System (WIMS) is an integrated database for all water related data. It is developed and maintained by National Water Informatics Centre (NWIC). WIMS is for authorized users only.
Click here to Visit WIMS Portal
4. Water Level Data:
For easy access, water level data from all four measurements conducted throughout the year since 1994 have been extracted and compiled below:
- January ground water level data 1994-2024
- April/May ground water level data 1994-2003
- April/May ground water level data 2004-2013
- April/May ground water level data 2014-2024
- August ground water level data 1994-2023
- November ground water level data 1994-2023












